Search Intent and Semantic Search: The SEO Buzzwords for 2021
While search engines are constantly trying to figure out what their users are actually looking for when they use a particular phrase, SEO is trying to figure out how search engines use their findings to rank websites.
In the early days of search, SEO was mainly about identifying the right keywords that would enable a website to rank higher. Use the right keywords and their variations generously throughout your website content and watch it climb to the top of the SERPs. (Yes, backlinks played a vital role too, but that’s not what this post is about!)
This led to a proliferation of black hat SEO techniques like “keyword stuffing”. Websites that used these techniques were soon “blacklisted” and penalized by search engines. They paid the price by getting pushed down further in the search results.
Search engine algorithms have made a lot of progress since then. With each new iteration, search engines are evolving and getting better at understanding natural human language. The latest sophisticated search algorithms are now able to understand the context and the intent behind a search phrase. They achieve this by using semantic search principles.
What are Semantic Search and Search Intent?
Search intent and semantic search are closely linked, in that semantic search is about identifying user intent. In other words, semantic search looks at a phrase and tries to understand the purpose or the reason for the particular search.
For instance, when a user searches for “xmas cake store”, the search engine needs to understand whether the user is looking for how to store xmas cakes or for stores where they can buy them.
Search algorithms need to understand not just the words themselves, but also the relationships between the words and their contextual meanings. Semantic search uses more than just the keywords in order to predict what a user might be looking for. Search engines may also use information about the user’s past searches, seasonal trends, local search trends, spelling variations and synonyms, and so on, while matching search queries to results pages.
In the case of “xmas cake store”, perhaps this particular user’s last ten searches have been for how to store rather than stores. The search engine uses that information to throw up pages related to storing cakes higher than those of stores. Or perhaps in that area more people search for stores rather than cake storage, in which case more pages related to stores would show up.
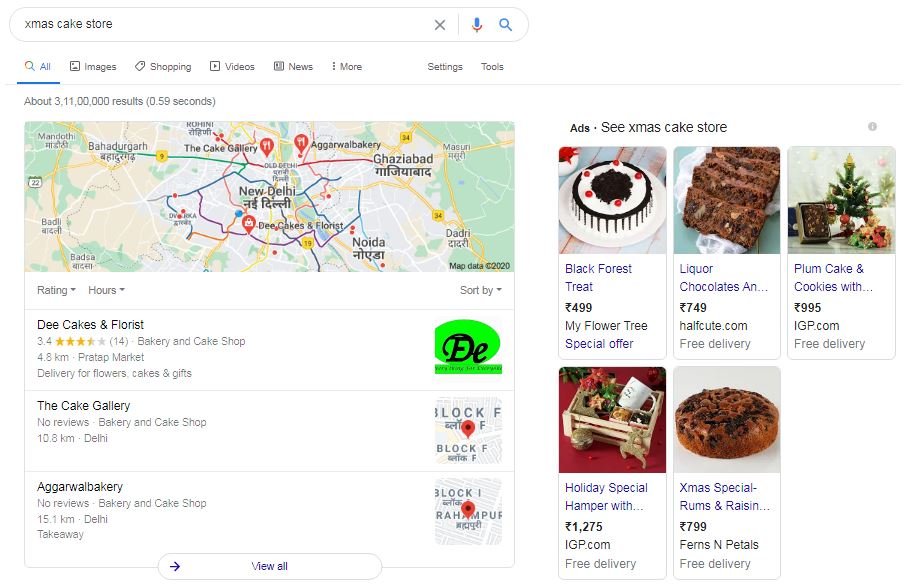
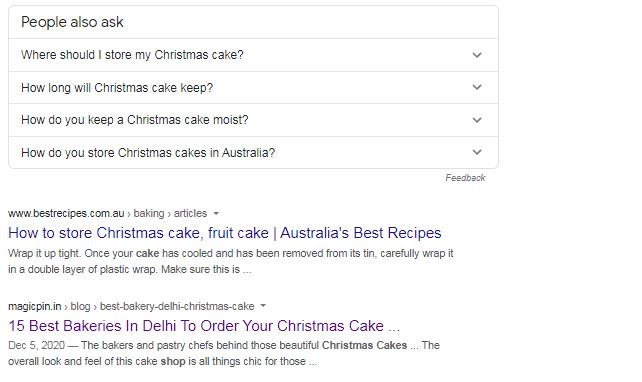
My search gave me mixed results: there were listings for local and online cake stores as well as results for how to store Christmas cakes. If you have an online cake store you could add your website to the Google Local listings and My Business pages so that it shows up when someone in your area searches for a product you sell.
Sometimes, the same word could have two or more connotations, like the brand name “Firefox” could stand for the bicycle store or for the web browser. In that case, the search engine would need to look at the words that precede or follow it in order to work out which product is being searched for. For instance, if the search term was “where can I download firefox”, the SERP would more likely show the results relating to the browser, whereas if the search term was “where can I buy firefox”, the SERP may show the results of the bicycle brand.
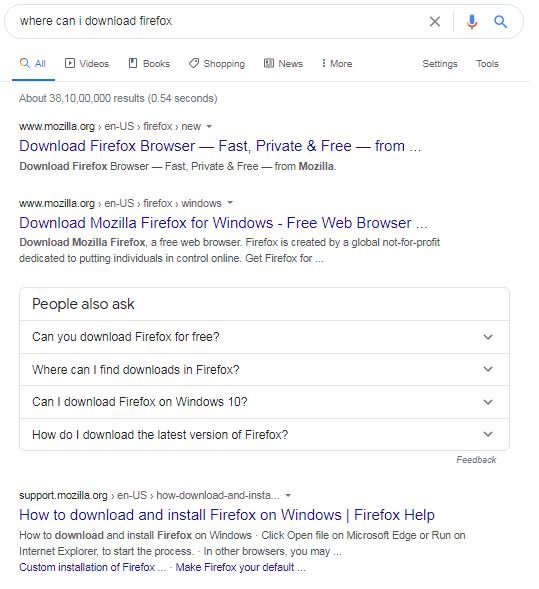
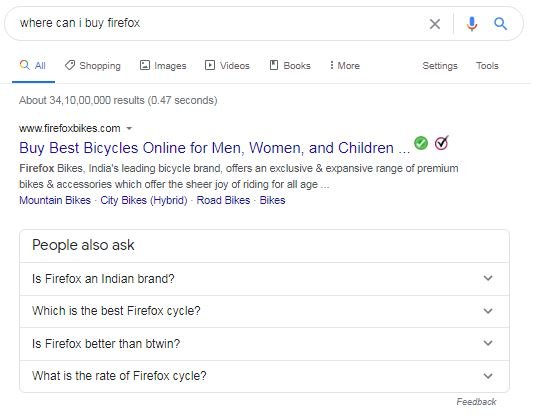
My search for "firefox" gave me very mixed results but when I added the terms "download" or "buy" the pages shown were very different. If you owned a brand website which could be confused for another, you could look at creating focused content and FAQs that answer specific questions users might have, so that you show up for the right search terms.
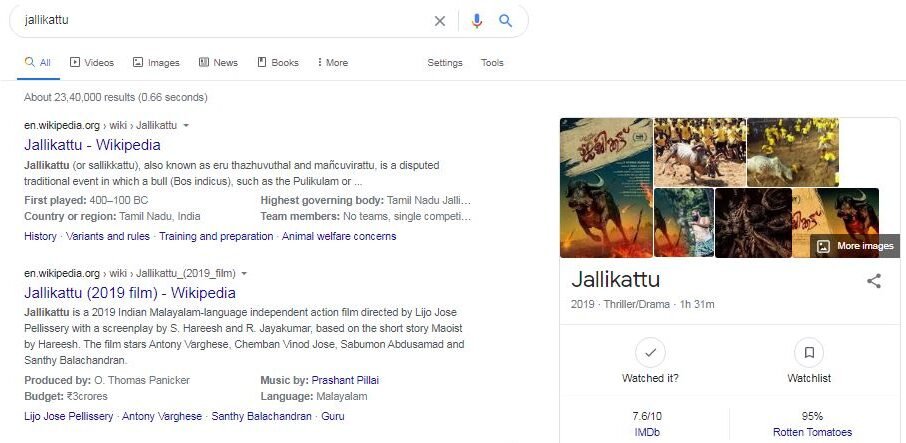
Let's look at another page of results for the term “jallikattu”. The term throws up pages both for the Malayalam movie "Jallikattu" and the bull racing event prevalent in Tamil Nadu. The "Knowledge Graph" on the right is Google's way of making some information stand out and easier for search engine users to find. You can use Schema and Structured Data Markups to make sure the relevant data on your site is found by the search engines.
How to Use Semantic Search to Extract the Most Out of Your SEO Effort
Semantic Search is just the first step of getting search engines to understand natural language. There will be many more advances and changes to the search algorithms as technology improves.
While it doesn’t change the fact that great content is still the best way to appear higher in the SERPs, there are a few ways to use search intent and semantic search in your SEO plan to increase visibility and improve rankings. And the search results page is a great resource for identifying what content people are looking for.
To summarize, here are some ways that you can use Semantic Search and Search Intent to your advantage and extract the most out of your SEO effort:
1. Create content based on search intent. Think about what a user may be intending to do when they use a particular term. Is it for research, for comparison, or for purchase? Are they just looking for information on a brand or are they looking for the website? In the “xmas cake store” example, if you sell xmas cakes, perhaps it makes sense to add some information on how to store the cakes once they are bought.
2. Create high quality, focused content. While keywords still matter, what’s more important is having content that is focused around a single topic with specific meaning. You can identify more relevant topics from the “related searches” section.
3. Create content that answers specific questions. If you look at the “People also ask” section of the SERP, you will see the top questions users have on related search terms. Use that to create an FAQ page.
4. Use schemas and structured data markups to highlight specific types of content. For instance, if you had a movie review site, you can use the ‘review’ schema options or add a ‘review snippet’ code to your page to enable search engines to find the right information faster.
If you're looking for professional SEO advice, our team at Truly Converting Content can help! Contact us for more information.
